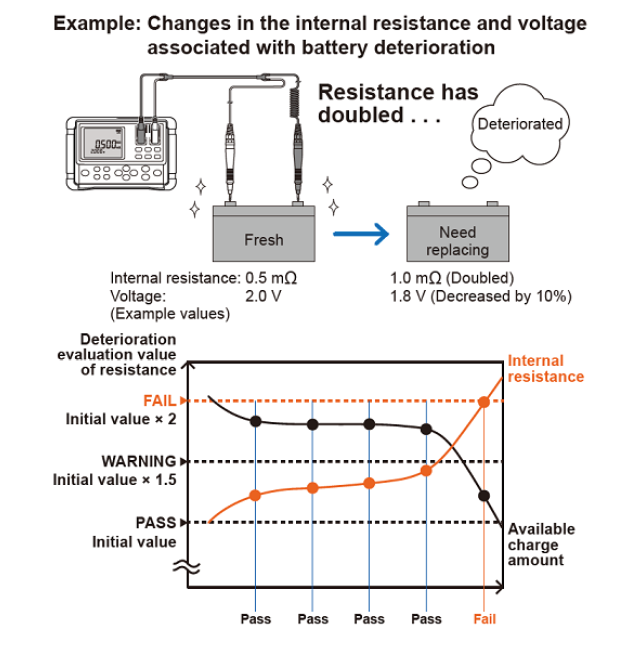
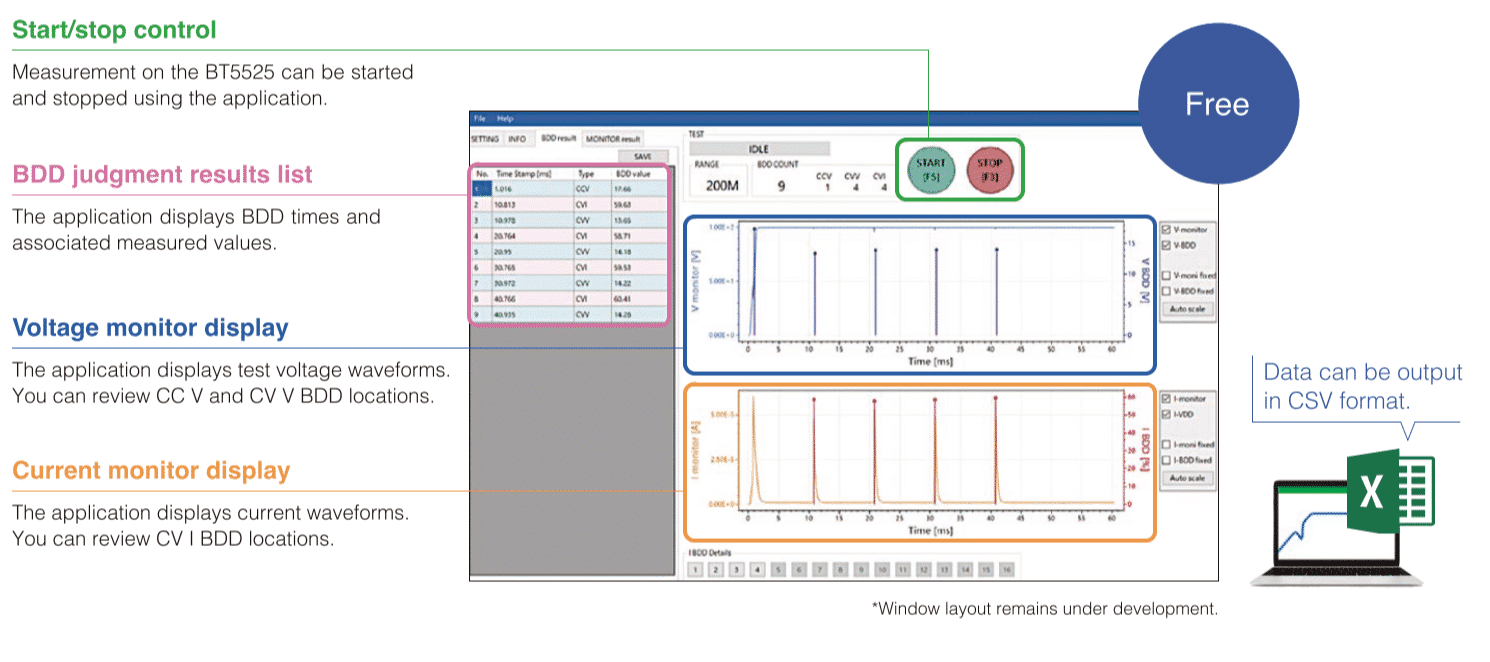
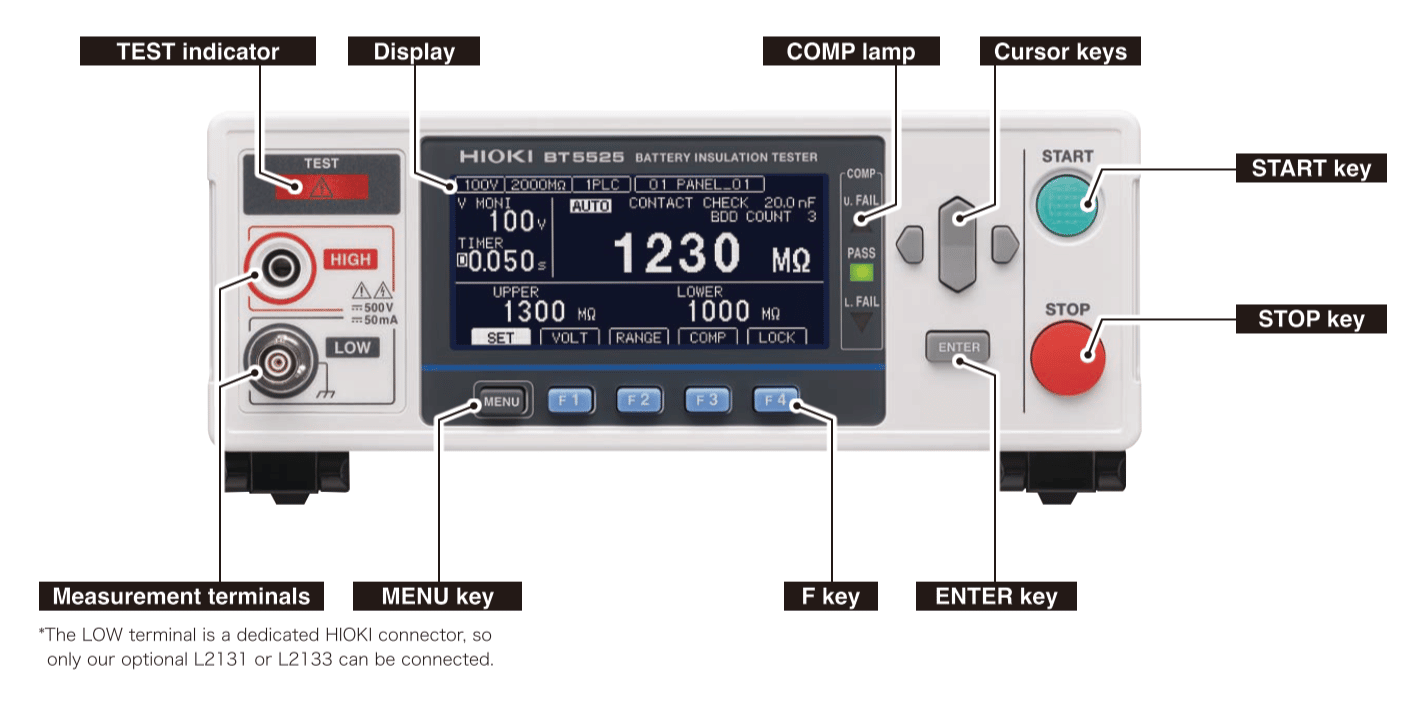
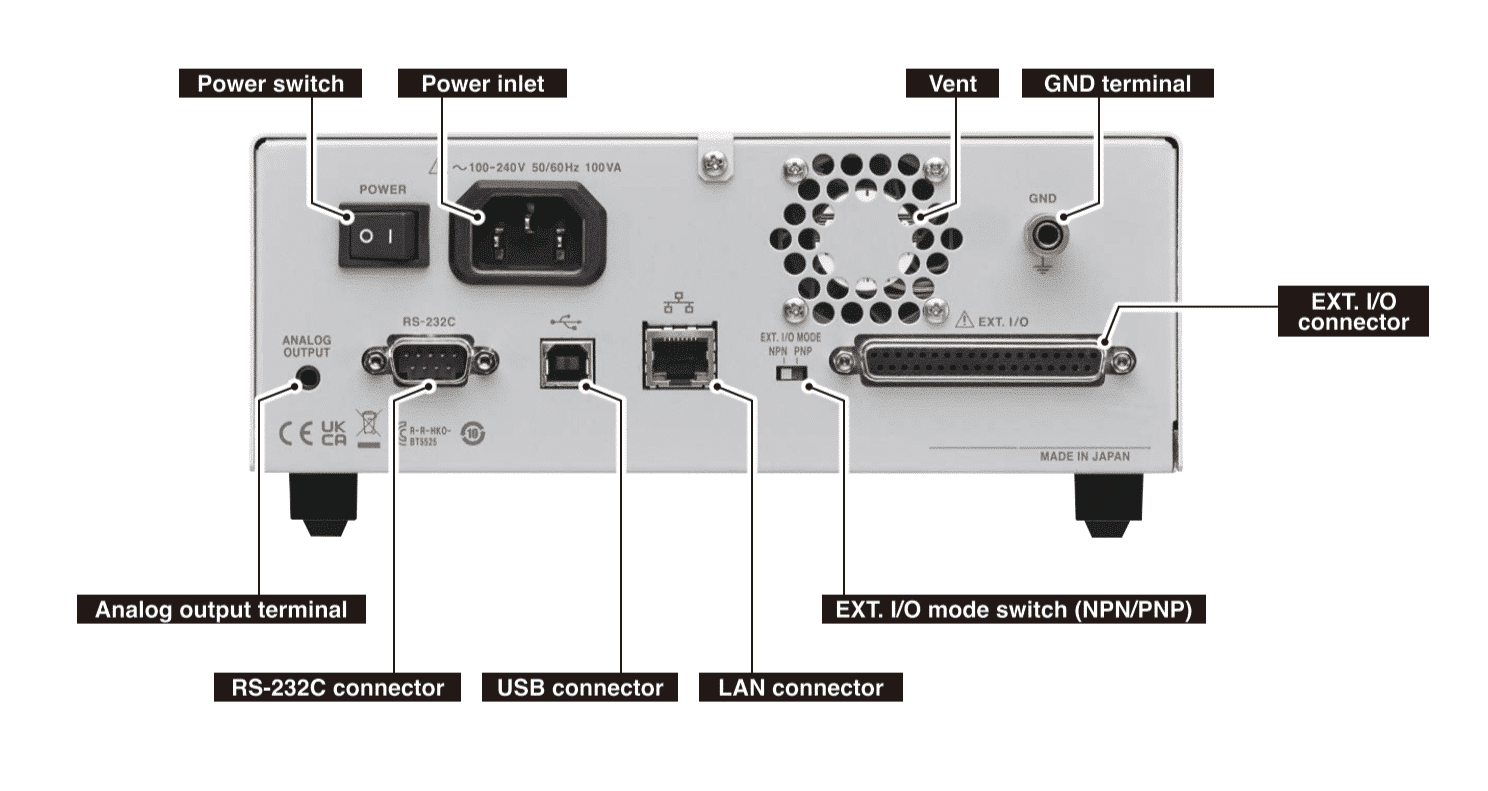
Measuring DC resistances is one of the functions pretty much every bench multimeter provides. Then why you would you need a separate resistance meter?
One of the best digital multimeters available on the market offers a lowest resistance range of 1 Ohm. This feature is highly advantageous for circuit development and PCB testing purposes.
However, when measuring the electrical resistance of conductive materials or welding contacts, you are looking at values which are more in the mOhm or µOhm range.
That’s why the “smallest” bench resistance meter from HIOKI – the RM3544 – has the lowest resistance range of 30 mOhm. Its “bigger brother”, the RM3545, has the lowest resistance range of 10 mOhm and a resolution of just 0.01 µOhm.
High speed measurements in small resistance ranges
Multimeters are not necessarily optimised to perform measurements at high speed. HIOKI’s resistance meters, on the other hand, have been designed to also perform resistance measurements in mass production environments where speed is an important factor. For example, when a module of lithium-ion batteries is produced then typically the quality of every spot weld connection to the busbar is tested by measuring the contact resistance. The RM3545 can perform such a measurement in its smallest 10 mOhm resistance range in just 41 ms (fast mode). In higher resistance ranges the measurement time is as low as 2.2 ms.
A very useful function (which is hard to find, even in top-of-the-range multimeters) is a contact check function. If activated, a measurement is only started after ensuring that the probe has proper contact to the device under test. This is a feature not necessarily critical in a lab environment, but really useful in production environments where it helps to avoid rejects caused by poor contact of the probe to the DUT. Please note, the contact check function is available on the RM3545, but not the RM3544 or RM3544-01.
Coming back to the example with the busbar welds of the battery module
The longest time in a test process is needed for mechanically moving the DUT to the test probe or test fixture. Once positioned, you want to perform as many tests as possible before having to mechanically move the DUT again.
This is where multiplexers come into play, especially when the number of tests to be performed is high. Dedicated multiplexers like HIOKI’s SW1002 provide the required number of measurement channels. If the number of channels is 20 or less, then such a dedicated multiplexer unit isn’t required.
In this case the RM3545-02 offers two slots on the backside that can each hold a multiplexer card Z3003. Each of these multiplexer cards offers 10 measurement channels for 4-wire measurements and they can easily be added to the RM3545-02 models. Please note, you can only add multiplexer cards to the RM3545-02 model.

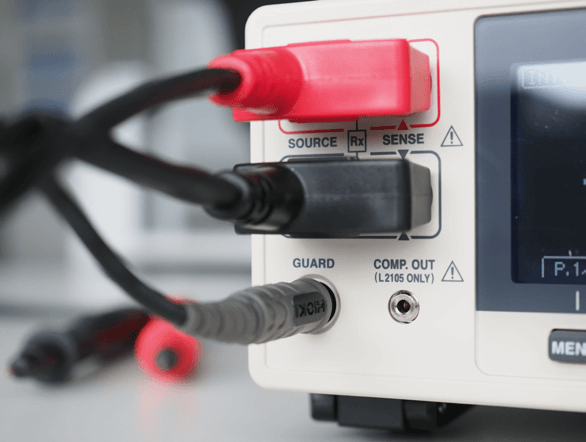
4-wire measurements usually mean 4 connectors at the measurement instrument for the test lead. However, if you look closely at the RM3544 or RM3545 you will see 5 connectors instead of 4. The 5th connector is the so-called “guard terminal”, which is designed to reduce measurement noise that can become relevant especially when test currents are small, i.e. in the high resistance ranges.
Technically the guard terminal allows to “ground the shield” of the test lead. The guard terminal is supported in HIOKI’s test leads L2101, L2102 , L2103 and L2104. Of course, you can also use test leads with the RM3544 and RM3545 that don’t connect to the guard terminal, such as HIOKI’s test leads L2100 or L2107.
Especially when you intend to measure small resistances then the test currents are high and the impact of noise is low. But again, especially in the MOhm resistance ranges not using the guard terminal can impact the measurement results.
The temperature sensor Z2001 is not just a nice add-on that allows you to also read the temperature when making a resistance measurement. Instead, it corrects the measured resistance value by taking into account a user-specific resistance temperature coefficient. This is especially useful when measurements can’t be performed in a temperature controlled environment.
The Z2001 temperature sensor is an included accessory of the RM3545 models and an option for the RM3544.
Another useful accessory - LED Comparator Attachment L2105
It indicates judgment results with green and red LEDs, eliminating the need to look at the instrument’s screen. Since the lamps do not light up when the measurement leads are open, this little optional accessory can also be used to ensure a proper connection to the DUT.

And finally, should you have an application which does require a measurement instrument with a low resistance range but at the same time doesn’t allow you to use a bench resistance meter, then HIOKI’s RM3548 might be the solution, it is portable, yet still features a smallest resolution of just 1 µOhm and offers a smallest measurement range of only 3 mOhm.
HIOKI RM3548 Portable Resistance Meter

The RM3548 doesn’t feature a guard terminal, as this portable resistance meter is typically used for lower resistances. Lower resistances mean that predominantly higher measurement currents are used for the measurements, making the “grounding of the shield” of the test lead unnecessary.
Also, while the above mentioned RM3545 resistance meter has a largest resistance range of 1200 MOhm, the RM3548‘s largest resistance range is “just” 3.5 MOhm.
Like the bench models RM3544 and RM3545, the RM3548 also supports the L2105 Comparator Attachment. And like the bench models the RM3548 offers a temperature correction and temperature conversion function. That said, bear in mind that the temperature sensor for the RM3548 is called Z2002, which is a different one than the Z2001 used for the bench models.
Conclusion
Multimeters without any doubt offer a huge range of functions that make it one of the most important test tools on a lab bench. At the same time there are requirements where dedicated resistance meters can make a real difference.
Downloads
MDL's range of Hioki Resistance Meters
Measuring resistance is essential in the design, development, and maintenance of electrical circuits and systems.
As official HIOKI distributors for the UK & IE, MDL Technologies offers a wide range of HIOKI Resistance Meters and Battery Testers. View our full range below. Alternatively, you can contact a member of our team for expert technical advice and product support.