TEM Devices /
GTEM Test Cells
GTEM (Gigahertz Transverse Electromagnetic) test cells are a type of electromagnetic shielding enclosure used for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing. These test cells are designed to simulate the electromagnetic environment in which electronic devices operate, and to evaluate their ability to operate in the presence of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The GTEM cell consists of a metal enclosure with a tapered opening at one end, and a coaxial cable connected to the other end. The interior of the enclosure is coated with a conductive material to prevent electromagnetic waves from entering or exiting the enclosure. The tapered opening provides a smooth transition from the coaxial cable to the interior of the enclosure, allowing electromagnetic waves to propagate into the enclosure.
GTEM test cells are used to test electronic devices for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) compliance. This involves subjecting the device under test (DUT) to electromagnetic fields of known frequency and intensity, and measuring its response. The response may be in the form of emissions (radiated or conducted) or susceptibility (the DUT's sensitivity to electromagnetic fields).
GTEM cells are advantageous for EMC testing because they offer a controlled, repeatable, and uniform electromagnetic environment. The tapered opening provides a consistent transition from the coaxial cable to the test volume, which minimizes reflections and standing waves that can affect the accuracy of test results. Additionally, GTEM cells have a wide operating frequency range and can generate high-intensity electromagnetic fields, making them suitable for testing a wide range of electronic devices.
GTEM (Gigahertz Transverse Electromagnetic) test cells are a type of electromagnetic shielding enclosure used for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing. These test cells are designed to simulate the electromagnetic environment in…
...which electronic devices operate, and to evaluate their ability to operate in the presence of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The GTEM cell consists of a metal enclosure with a tapered opening at one end, and a coaxial cable connected to the other end. The interior of the enclosure is coated with a conductive material to prevent electromagnetic waves from entering or exiting the enclosure. The tapered opening provides a smooth transition from the coaxial cable to the interior of the enclosure, allowing electromagnetic waves to propagate into the enclosure.
GTEM test cells are used to test electronic devices for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) compliance. This involves subjecting the device under test (DUT) to electromagnetic fields of known frequency and intensity, and measuring its response. The response may be in the form of emissions (radiated or conducted) or susceptibility (the DUT’s sensitivity to electromagnetic fields).
GTEM cells are advantageous for EMC testing because they offer a controlled, repeatable, and uniform electromagnetic environment. The tapered opening provides a consistent transition from the coaxial cable to the test volume, which minimizes reflections and standing waves that can affect the accuracy of test results. Additionally, GTEM cells have a wide operating frequency range and can generate high-intensity electromagnetic fields, making them suitable for testing a wide range of electronic devices.
-
ETS-Lindgren’s GTEM!™ Test Cell enables users to perform radiated emissions and radiated immunity tests in less time than at either an...FIND OUT MORE
-
ETS-Lindgren’s GTEM!™ Test Cell enables users to perform radiated emissions and radiated immunity tests in less time than at either an...FIND OUT MORE
-
ETS-Lindgren’s GTEM!™ Test Cell enables users to perform radiated emissions and radiated immunity tests in less time than at either an...FIND OUT MORE
-
ETS-Lindgren’s GTEM!™ Test Cell enables users to perform radiated emissions and radiated immunity tests in less time than at either an...FIND OUT MORE
-
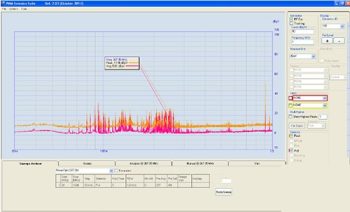
The PMM Narda Emission Suite is a very powerful software tool specifically designed to operate a wide range of PMM EMI Receivers, which could differ...FIND OUT MORE